Sunday, April 4, 2010

Choosing a Commercial Web Host
Below are some criteria when choosing commercial web host. For more info, u can go to http://www.thesitewizard.com/archive/findhost.shtml
- Reliability and speed of access
- Data Transfer (Traffic/Bandwidth)
- Disk space
- Technical support
- FTP, PHP, Perl, SSI, .htaccess, telnet, SSH, MySQL, crontabs
- SSL (secure server), Shopping Cart
- Email, Autoresponders, POP3, Mail Forwarding
- Control Panel
- Multiple Domain Hosting and Subdomains
- Server
- Price
- Monthly/Quarterly/Annual Payment Plans
- Resellers?
- International
Choosing a Free Web Host
1. Advertising
Most free web hosts impose advertising on your website. This is done to cover the costs of providing your site the free web space and associated services. Some hosts require you to place a banner on your pages; others display a window that pops up every time a page on your site loads, while still others impose an advertising frame on your site. Whichever method is used, check that you're comfortable with the method.
Note that free web hosts without forced advertisements aren't necessarily good news. Without a viable means to recover the costs of running their server, many of them close with alarming frequency.
2. Amount of web space
Does it have enough space for your needs? If you envisage that you will expand your site eventually, you might want to cater for future expansion. Most sites use less than 5MB of web space. Indeed, at one time, one of my other web sites, thefreecountry.com, used less than 5MB of space although it had about 150 pages on the site. Your needs will vary, depending on how many pictures your pages use, whether you need sound files, video clips, etc.
3. FTP access
(In case you're wondering: What is FTP?)
Some free hosting providers only allow you to design your page with their online builder. While this is useful for beginners, do you have the option to expand later when you become experienced and their online page builder does not have the facility you need? FTP access, or at the very least, the ability to upload your pages by email or browser, is needed. Personally, I feel FTP access is mandatory, except for the most trivial site.
4. File type and size limitations
Watch out for these. Some free hosts impose a maximum size on each of the files you upload (including one with a low of 200KB). Other sites restrict the file types you can upload to HTML and GIF/JPG files. If your needs are different, eg, if you want to distribute your own programs on your pages, you will have to look elsewhere.
5. Reliability and speed of access
This is extremely important. A site that is frequently down will lose a lot of visitors. If someone finds your site on the search engine, and he tries to access it but find that it is down, he'll simply go down the list to find another site. Slow access is also very frustrating for visitors (and for you too, when you upload your site). How do you know if a host is reliable or fast? If you can't get feedback from anyone, one way is to try it out yourself over a period of time, both during peak as well as non-peak hours. After all, it is free, so you can always experiment with it.
6. Perl and PHP
(In case you're wondering: What is PHP and Perl?)
This is not particularly crucial nowadays for a free web host, since there are so manyfree script hosting services available that provide counters, search engines, forms,polls, mailing lists, etc, without requiring you to dabble with Perl or PHP scripts.
However if you really want to do it yourself, with the minimum of advertising banners from these free providers, you will need either PHP or Perl access. Note that it is not enough to know they provide PHP or Perl access: you need to know the kind of environment your scripts run under: is it so restrictive that they are of no earthly use? For PHP scripts, does your web host allow you to use the mail() function? For Perl scripts, do you have access to sendmail or its workalike?
7. Bandwidth allotment
Nowadays, many free web hosts impose a limit on the amount of traffic your website can use per day and per month. This means that if the pages (and graphic images) on your site is loaded by visitors beyond a certain number of times per day (or per month), the web host will disable your web site (or perhaps send you a bill). In general, 100MB traffic per month is too little for anything other than your personal home page and 1-3GB traffic per month is usually adequate for a simple site just starting out. Your mileage, however, will vary.
We supposed to present our final project today but due to some problem we all agreed to postpone it to Monday next week. So just be prepared!!
Ops..class got cancel again. Good thing though. We have more time doing our website..hehe
FIVE CRITERIA are:
Accuracy of Web Documents
- Who wrote the page and can you contact him or her?
- What is the purpose of the document and why was it produced?
- Is this person qualified to write this document?
Authority of Web Documents
- Who published the document and is it separate from the "Webmaster?"
- Check the domain of the document, what institution publishes this document?
- Does the publisher list his or her qualifications?
Objectivity of Web Documents
- What goals/objectives does this page meet?
- How detailed is the information?
- What opinions (if any) are expressed by the author?
Currency of Web Documents
- When was it produced?
- When was it updated'
- How up-to-date are the links (if any)?
Coverage of the Web Documents
- Are the links (if any) evaluated and do they complement the documents' theme?
- Is it all images or a balance of text and images?
- Is the information presented cited correctly?
Putting it all together
- Accuracy. If your page lists the author and institution that published the page and provides a way of contacting him/her and . . .
- Authority. If your page lists the author credentials and its domain is preferred (.edu, .gov, .org, or .net), and, . .
- Objectivity. If your page provides accurate information with limited advertising and it is objective in presenting the information, and . . .
- Currency. If your page is current and updated regularly (as stated on the page) and the links (if any) are also up-to-date, and . . .
- Coverage. If you can view the information properly--not limited to fees, browser technology, or software requirement, then . . .
Why do we need to do web testing and evaluation?
Web Evaluation – Focus more on non technical part, outcome.
- Website effectiveness: First, you should measure effectiveness in terms of visitors’ experiences on your website. For example, you can measure how many people visit your site, how satisfied they are, and how well they’re able to accomplish what they want. The jargon for this kind of measurement is “Web metrics” or “Web analytics.” Read more about different types of website evaluation.
- Achievement of agency mission: Second, you should measure the impact of your website on achievement of your agency’s mission. These performance measures address the extent to which your agency is achieving its mission specifically because of its website. Read more about tying evaluation to agency mission.
This week every group had presented their 40% of project in front of class. From there we can do some correction based on comments from Dr J and other fellow friends. Dr J gave us an evaluation form to make our own comments on the presentation for each group.
We supposed to present our 40% of project this week. But we postponed it to next week. So today we have lectured as usual and today’s topic is Visual Design in website.
Visual design means that the planning on how your website will look like. You must consider the color, font or styles, graphic and multimedia that you will use on your website. Last but not least you must find the way how all of these elements will be combined or arrange into an attractive layout.
There are several elements of user interface such as
- · Background that reflect the theme
- · Foreground elements that reflect the theme
- · Other elements (text, images, buttons, animation, etc) that support the theme
When you choose the typography, make sure it simple and readable for user.
There are some tools that we use in visual design to help us see more the design for a first start.
Thumbnails Sketches - Help designer think about the visual aspects of the web pages they are designing and help make choices about web site’s presentation design.
Storyboard vs Thumbnails Sketches?
Storyboard – helps on web site’s interaction.
Thumbnails – help to focus on how web pages will look.
Rough Sketches - Usually choose 2 or 3 of the thumbnails to develop further. This more developed sketch is called rough sketches. More carefully drawn – proportions are more accurate.
What is good design? It’s a seemingly simple question that’s surprisingly difficult to answer. The more you think about it, the more complex the question becomes. Not only does “good design” mean different things to different people, it also changes at different times and in different contexts.
Some of the world’s leading designers were challenged to define what “good design” means now in a debate at the annual meeting of the World Economic Forum in Davos last week. At the debate, which I moderated, each designer was asked to identify one example of “good” and one example of “bad” design, and to explain the reasons for the choices. What did they come up with?
Please go to this site to read more..it such a good writing..
http://dealbook.blogs.nytimes.com/2009/01/31/defining-good-or-bad-design/
This week we learned about Interaction Design..hmm..what does it mean by Interaction Design. Why don't we go trough some definition first to get some brief idea about the topic.
This definition of interaction from Dix et al. is representative of these texts, and the field:
By interaction we mean any communication between a user and computer, be it direct or indirect. Direct interaction involves a dialog with feedback and control throughout the performance of the task. Indirect interaction may involve background or batch processing. The important thing is that the user is interacting with the computer in order to accomplish something. (Dix et al., 1998, p. 3)
Interaction Design got related to the interactivity. Interactivity in a computer products means that the user, not the designer, controls the sequence, the pace, and most importantly, what to look at and what to ignore.
The following principles are fundamental to the design and implementation of effective interfaces, whether for traditional GUI environments or the web. Of late, many web applications have reflected a lack of understanding of many of these principles of interaction design, to their great detriment. Because an application or service appears on the web, the principles do not change. If anything, applying these principles become even more important.
Anticipation, Autonomy, Color Blindness, Consistency, Default, Efficiency of the user, Explorable interfaces and etc.
Go to AskTog site to get more info. Hope it will add some new knowledges to u guys..!!
Saturday, April 3, 2010
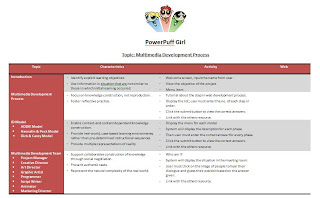
Thursday, April 1, 2010
For today's class, Dr J gives us some time to discussed about our upcoming final project. Forgot to mention my group members. :) Mia group members are kak Madihah, Fazlinda n Zarena. Together we are "PowerPuff Girls"(saying it with enthusiasm).






